Farm disinfection plays a critical role in maintaining the health and productivity of livestock and crops, particularly in an era where agricultural operations are increasingly challenged by disease outbreaks and pest infestations. According to a report by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), biosecurity measures, including effective disinfection protocols, can reduce disease incidence in livestock by up to 50%, significantly impacting overall farm productivity. This highlights the importance of adopting comprehensive and effective farm disinfection methods to safeguard animal health and crop yields from potential pathogens.
Moreover, the economic implications of poor disinfection practices can be staggering. The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) estimates that livestock diseases, many of which can be mitigated through proper sanitation protocols, cost the industry billions annually in lost productivity and treatment expenses. Therefore, understanding and implementing the best farm disinfection methods is vital not just for enhancing biosecurity but also for ensuring sustainable agricultural practices that contribute to food safety and public health. In the sections that follow, we will explore ten of the most effective farm disinfection methods, backed by recent research and industry best practices, aimed at promoting healthier livestock and crops.
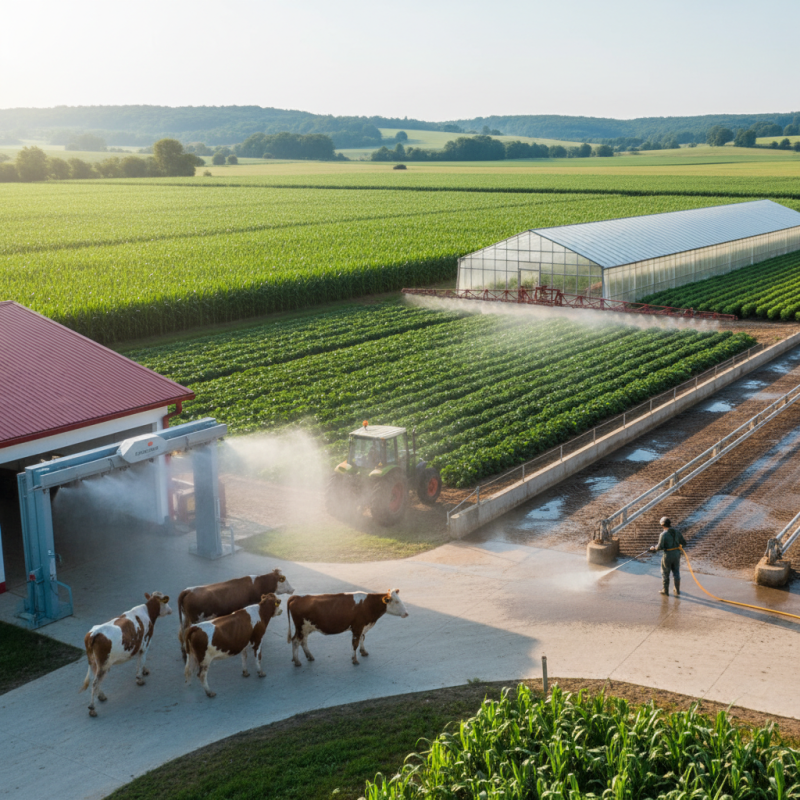

Farm disinfection plays a critical role in maintaining the health of both livestock and crops, serving as a proactive measure against the spread of diseases that can devastate production. According to the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE), infectious diseases contribute to significant financial losses in the agriculture sector, with economic impacts estimated to reach billions of dollars annually. Ensuring that farms utilize effective disinfection methods can mitigate these risks by reducing pathogen load in the environment, which is essential for thriving agricultural practices.
In a study published by the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), it was reported that farms that implement regular disinfection protocols experience up to a 30% decrease in disease prevalence among livestock. Maintaining a clean environment not only enhances animal health but also leads to improved crop yields. The interconnectedness of livestock health and crop production necessitates an integrated approach to farm management; for instance, pathogens can transfer from livestock waste to soil and crops, thereby creating a cycle of infection. By prioritizing disinfection, farmers can safeguard the overall health of their operations, contributing to a more sustainable agricultural landscape.
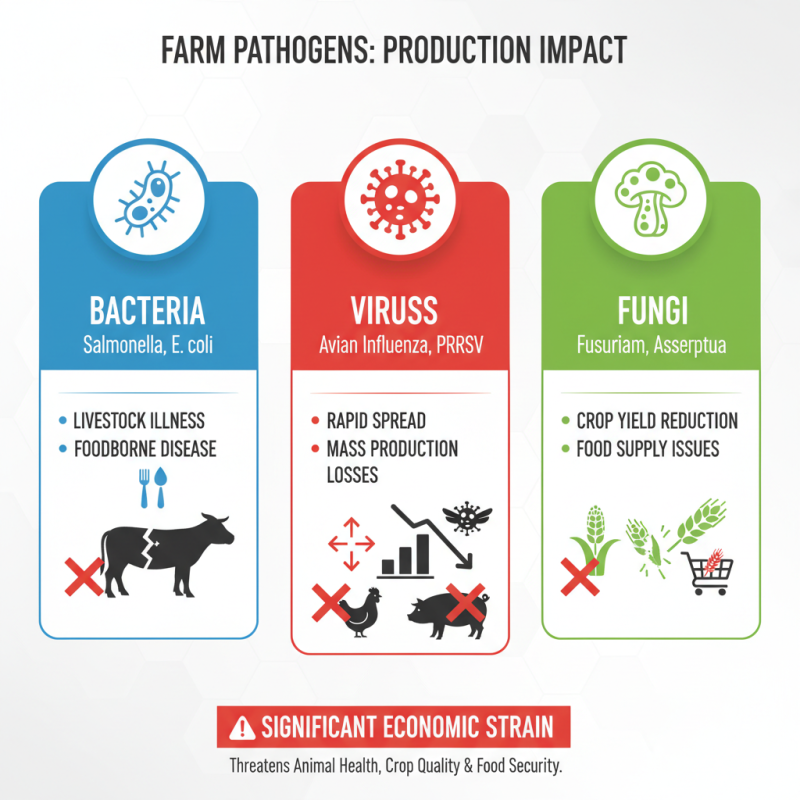
Farm production is significantly impacted by a variety of common pathogens, which can lead to diseases in both livestock and crops. Bacteria such as Salmonella and Escherichia coli are notorious for causing foodborne illnesses in animals and humans alike, affecting the overall health of livestock and the safety of food products. Viruses, such as the Avian Influenza virus and Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome virus, can spread rapidly in dense animal populations, leading to substantial losses in production. Fungal infections, including those caused by species like Fusarium and Aspergillus, can compromise crop yields and quality, leading to economic strain for farmers and food supply issues for consumers.
Understanding the various pathogens that threaten farm production is crucial for implementing effective disinfection methods. Regular monitoring and testing can help identify potential outbreaks before they escalate, allowing for timely interventions. Additionally, maintaining strict biosecurity measures, such as controlling access to farm areas and utilizing disinfection protocols, can significantly reduce the risk of pathogen transmission. Integrating these practices into farm management not only promotes healthier livestock and crops but also contributes to sustainable agricultural practices that protect the industry and the environment.
Disinfection in agriculture is crucial for maintaining the health of livestock and crops. Effective methods not only help prevent the spread of pathogens but also enhance overall productivity. One common method used in farms is the application of heat treatment, which involves exposing equipment and surfaces to high temperatures to eliminate harmful microorganisms. Additionally, vapourized hydrogen peroxide is gaining popularity due to its efficacy in disinfecting large areas without leaving harmful residues.
Another effective disinfection technique is the use of biodegradable disinfectants derived from natural sources. These eco-friendly solutions not only reduce the chemical load on the environment but also ensure the safety of livestock and crops. Furthermore, regular cleaning practices combined with the use of UV light can significantly lower the bacterial load in barns and greenhouses. By integrating these innovative disinfection methods, farmers can foster a healthier farming ecosystem and ultimately ensure better yields.
| Disinfection Method | Effectiveness | Application Area | Active Ingredients | Safety Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Disinfectants | High | Livestock housing | Chlorine, Quaternary Ammonium Compounds | Use with protective gear |
| Heat Treatment | Very High | Equipment and tools | N/A | Ensure no damage to equipment |
| Steam Disinfection | High | Soil and buildings | Steam | Avoid burns |
| Ultraviolet Light | Moderate | Water and surfaces | UV light | Protect eyes and skin |
| Hydrogen Peroxide | High | Surfaces and tools | Hydrogen Peroxide | Safe when properly diluted |
| Essential Oils | Moderate | Small-scale disinfection | Thyme, Oregano | May cause allergies |
| Iodine Solutions | High | Livestock and tools | Iodine | Use with caution on skin |
| Antimicrobial Foams | High | High-traffic areas | Various active ingredients | Ensure proper ventilation |
| Biosecurity Practices | Very High | Entire farm | N/A | Continuous implementation required |
| Cold Plasma Technology | Emerging | Air and surfaces | Cold plasma | Research ongoing |

Effective disinfection in farming is essential to maintaining healthy livestock and ensuring robust crop production. To implement successful disinfection methods, one can follow a structured approach. Start by preparing the area for disinfection—this involves removing debris, organic matter, and dirt, which can harbor pathogens. Thorough cleaning is a critical preliminary step that enhances the effectiveness of disinfectants. Use water and appropriate cleaning agents to scrub surfaces, focusing on high-touch areas such as feeding troughs, housing facilities, and equipment.
Once the area is cleaned, it’s time to select the appropriate disinfectant based on the pathogens targeted and the environment's specific needs. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for dilution and application—ensuring the disinfectant can effectively eliminate bacteria, viruses, and fungi present. Apply the disinfectant uniformly across all surfaces, allowing sufficient dwell time as specified to maximize the effectiveness. Regular rotation of different disinfectants can help in preventing the development of resistant pathogens. Finally, ensure proper drying and ventilation after disinfecting to maintain a safe environment for livestock and crops, minimizing any potential risks associated with residual chemicals.
Maintaining a disinfected farm environment is crucial for the health and productivity of both
livestock and crops.
One of the best practices is to implement a scheduled cleaning routine that includes
regular sanitization of equipment, animal housing, and any areas where feed and water are stored.
This helps to minimize the buildup of pathogens and reduces the risk of disease spread.
Utilizing biosecurity protocols, such as controlling access to sensitive areas of the farm and ensuring personnel
follow strict hygiene practices, can greatly enhance the overall sanitation efforts.
In addition to routine cleaning, selecting effective disinfection methods is vital.
Farmers should consider using environmentally friendly disinfectants
that effectively eliminate harmful microorganisms without posing risks to the ecosystem.
Proper application techniques, including adequate contact time and appropriate dilution, are critical to ensure
full effectiveness. Moreover, emphasizing crop rotation and
integrated pest management can naturally reduce the need for harsh chemicals
while promoting a healthier growing environment. By adopting these best practices, farmers can achieve
a holistic approach to maintaining disinfected farm environments that ultimately leads to
healthier livestock and more robust crops.






